CPX-AP-x-4IOL-M12: Working with OE variants in EtherNet/IP

Sandro Quintero, Mechatronics Technology Engineering Manager, Festo North America

TL;DR
When using a CPX-AP-x-4IOL-M12 module on an EtherNet/IP network, it is recommended to use the non-OE Variant for selecting the port size. This way, you won’t have to deal with OutputEnable.
Description of OE
When configuring the ports of an IO-Link master like CPX-AP-I-4IOL-M12 or CPX-AP-A-4IOL-M12, you will come across a parameter that specifies the number of bytes reserved per IO-Link port, known as the Variant.
Let’s discuss setting up an IO-Link module for 2 bytes per port in an EtherNet/IP (EP) network. As shown in Figure 1, we have two options: Variant 2 and Variant 2_OE, both of which are supported on EP. The main difference lies in the output size, with Variant 2_OE having an additional 4 bytes.
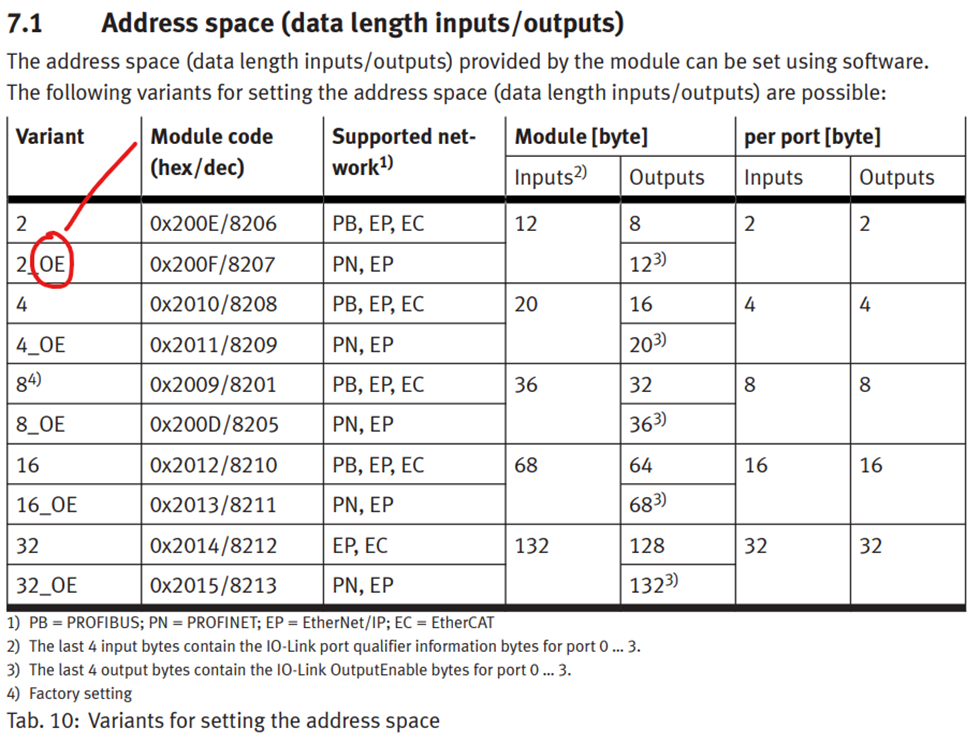
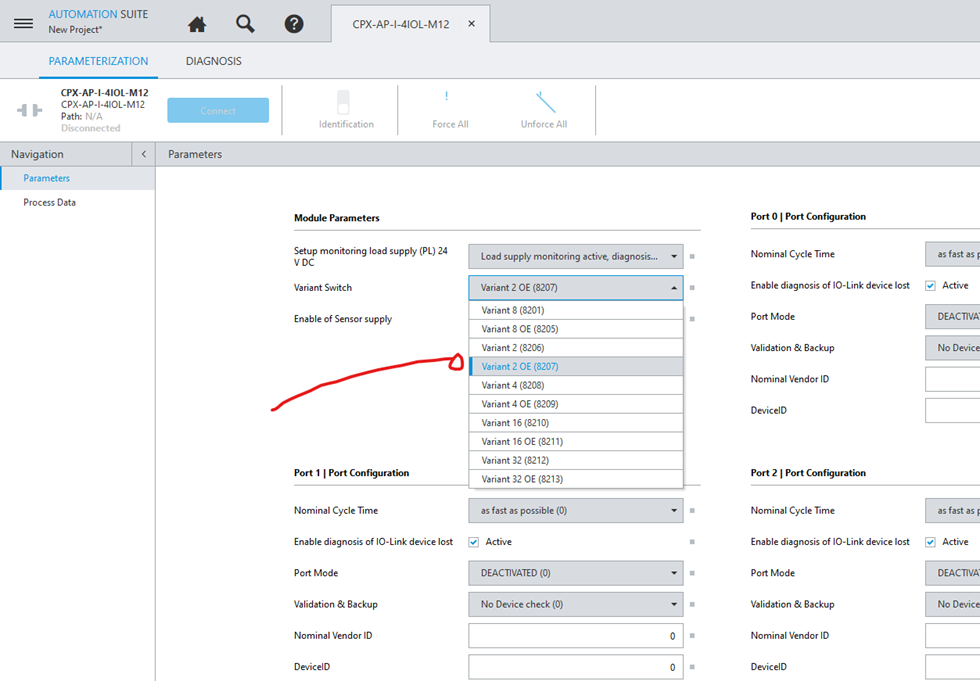
Figure 2 shows where the Variant is selected when using Festo Automation Suite (FAS), this can also be configured in the WebServer of the IO-Link module.
OE stands for Output Enable and is typically used when configuring the IO-Link master for a PROFINET (PN) network. However, it can also be used in an EtherNet/IP (EP) configuration.
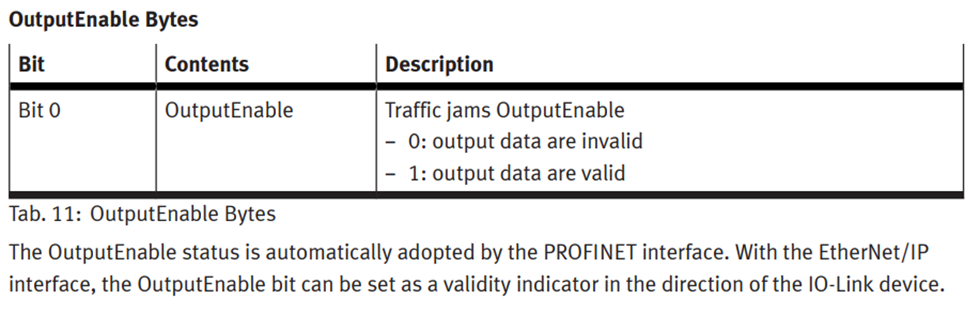
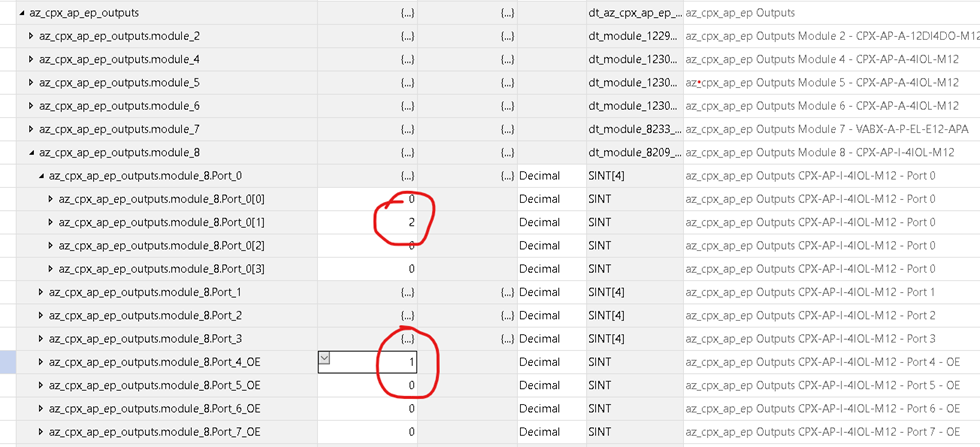
Recently, I encountered a case where the OE variant was selected, and when the user attempted to turn on the outputs on one of the ports of the IO-Link master, the PLC would receive the data, but nothing would happen. It was as if the data wasn’t being sent to the IO-Link device. This occurred because Bit 0 of the OutputEnable byte for that port was set to FALSE. Once that bit was set to TRUE, the data was successfully transmitted to the IO-Link device, Figure 4.
Links
For more information, you can refer to the user manual for the IO-Link module, which can be found here:
Disclaimer
This post is provided solely for the purpose of offering setup assistance and general guidance. It is important to note that the ultimate responsibility for ensuring the overall safety and proper functionality of the machine lies with the System Integrator / End User. It is crucial to exercise caution, adhere to proper safety protocols, and consult relevant experts or professionals when necessary.
Although Festo employees will be contributing to this blog, please note this is not the official Festo support channel. For more timely technical support please reach out to your regional Festo support channel and/or consult user manuals and relevant documentation in www.festo.com.
