Simplified Lubrication Schedule

Shane Roy, Mechatronics Application Engineer, Festo USA

Introduction
Linear actuators require periodic maintenance similar to other mechanical systems. Our products provide great documentation to identify when to perform this maintenance such as lubrication, belt replacement, and cleaning the axis. The frequency of this maintenance is dependent on the strain applied to the axis during operation. For example, an axis moving a higher load than a similar axis will require maintenance more frequently. For customers that need high accuracy for predicting maintenance, having a detailed equation for calculating this schedule is necessary. But, for other customers that want a rough estimate, the calculations can be cumbersome. The lubrication schedule can be simplified in this case to give a rough estimate for when the axis needs to be lubricated.
Example Lubrication Schedule
To provide an example for simplifying the lubrication schedule, assume using a Festo ELGD-TB-KF-…-GN axis. Within the Operating Instructions, chapter 8 provides information on maintenance. The lubrication interval (Sint) is dependent on the load comparison factor (fv) as shown in the graph below.
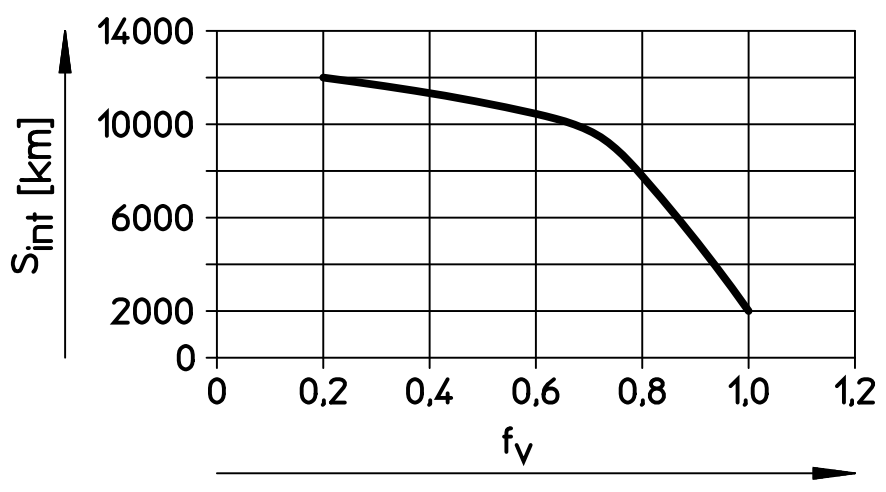
The documentation describes calculating this load comparison factor which is based on the forces and torques applied to the axis in each direction. The lubrication interval is also further derated based on other factors including debris in the environment, excessively long or short axes, temperature, and the age of the system.
For estimating the lubrication schedule where any maintenance is not a disruption in the production process, the load comparison factor can be simplified into three categories:
- Light Use (fv = 0.2)
- Normal Use (fv = 0.6)
- Heavy Use (fv = 1)
Determining which category your system falls into can be nuanced, with ‘Normal Use’ assuming that none of the maximum ratings listed in the datasheet are exceeded. This includes the feed force, speed, and acceleration. One method for determining the category can be based on the sizing report from Electric Motion Sizing. For example, the following selection of components from an Electric Motion Sizing report, demonstrates ‘Normal Use’ since the linear axis is only being utilized between 40-70%. This takes into account the load applied to the system and the move profiles set for the sizing report.
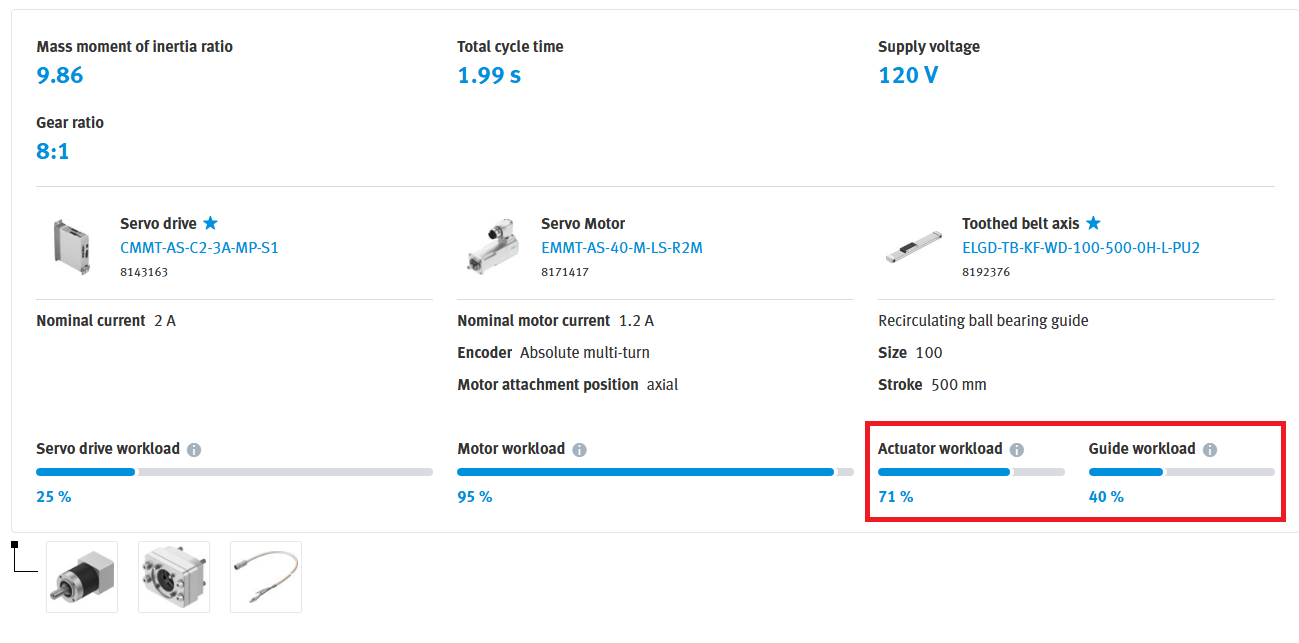
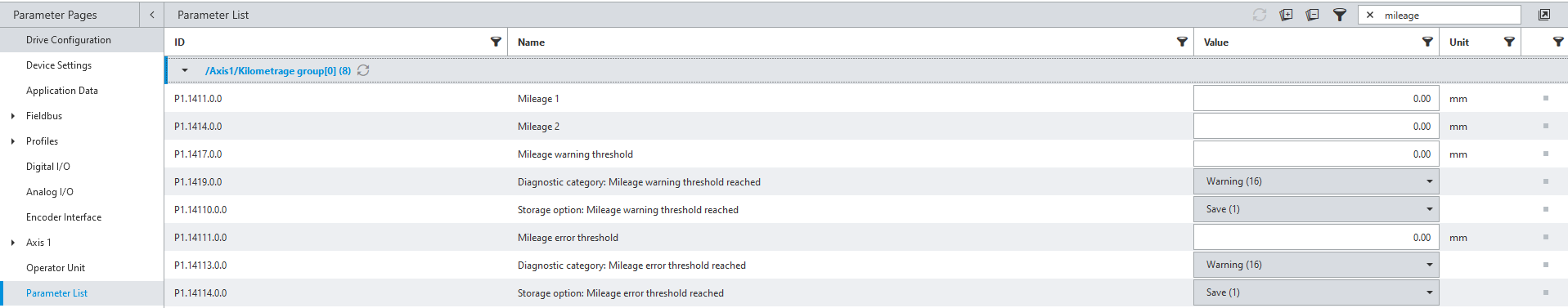
Based on Normal Use (fv = 0.6), I can estimate the axis will need to be lubricated about every 10.5km. To track this mileage, the CMMT-ST and CMMT-AS drives have mileage parameters that keep track of the total distance traveled by the axis. Also, notice additional parameters that can be configured to output a diagnostic warning when the mileage has reached a specified value.
See screenshot below from the Festo Automation Suite software:
Disclaimer
This post is provided solely for the purpose of offering setup assistance and general guidance. It is important to note that the ultimate responsibility for ensuring the overall safety and proper functionality of the machine lies with the System Integrator / End User. It is crucial to exercise caution, adhere to proper safety protocols, and consult relevant experts or professionals when necessary.
Although Festo employees will be contributing to this blog, please note this is not the official Festo support channel. For more timely technical support please reach out to your regional Festo support channel and/or consult user manuals and relevant documentation in www.festo.com
